Some related questions:
- How do you define Reasoning and Problem Solving?
- What do we need children to understand in order to evidence reasoning and problem solving?
- If reasoning and problem solving is associated with Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS) in Blooms Taxonomy, what is needed for there to be EQUITY for ALL children?
- What behaviours do we want children to demonstrate?
What teachers/adults can do:
- Listen carefully to what children are saying and encourage them to articulate their thinking – part of the Oracy approach
- Encourage children to use representatives and pictures to support their exploration, thinking and reflections – Manipulatives for Visualisation and SpacialReasoning
- Provide tasks and opportunities for children to demonstrate the behaviours proposed by Cuoco et al
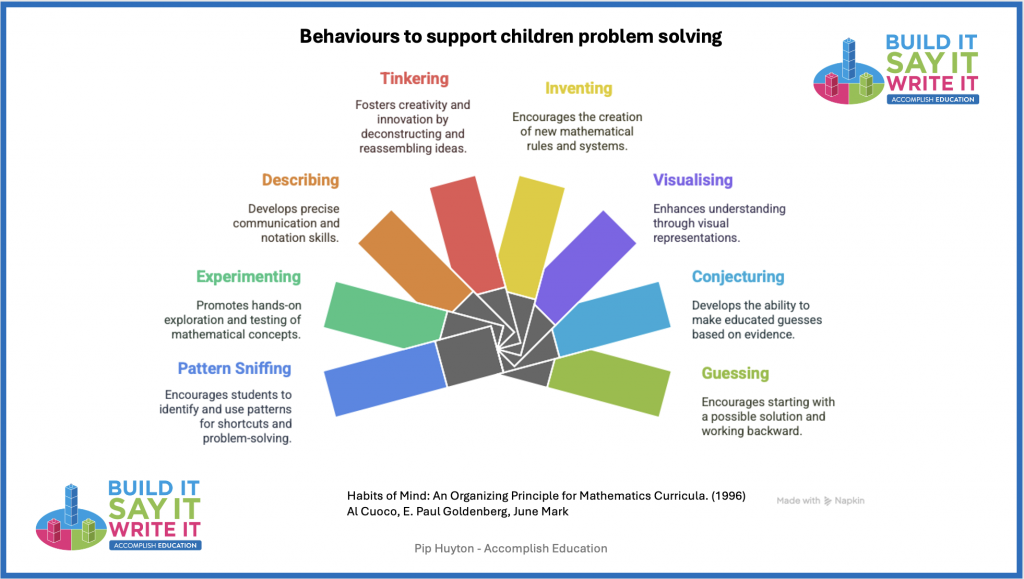
Nrich maths identifies the following approaches when working on problems:

Technology can support development of reasoning and problem solving, with the capability to:
- provide representations/manipulatives that may not in the moment be available in the physical form for visualisation
- record children’s approaches to the task, as they work – Strategy
- record children’s thoughts articulated as they are working -Oracy
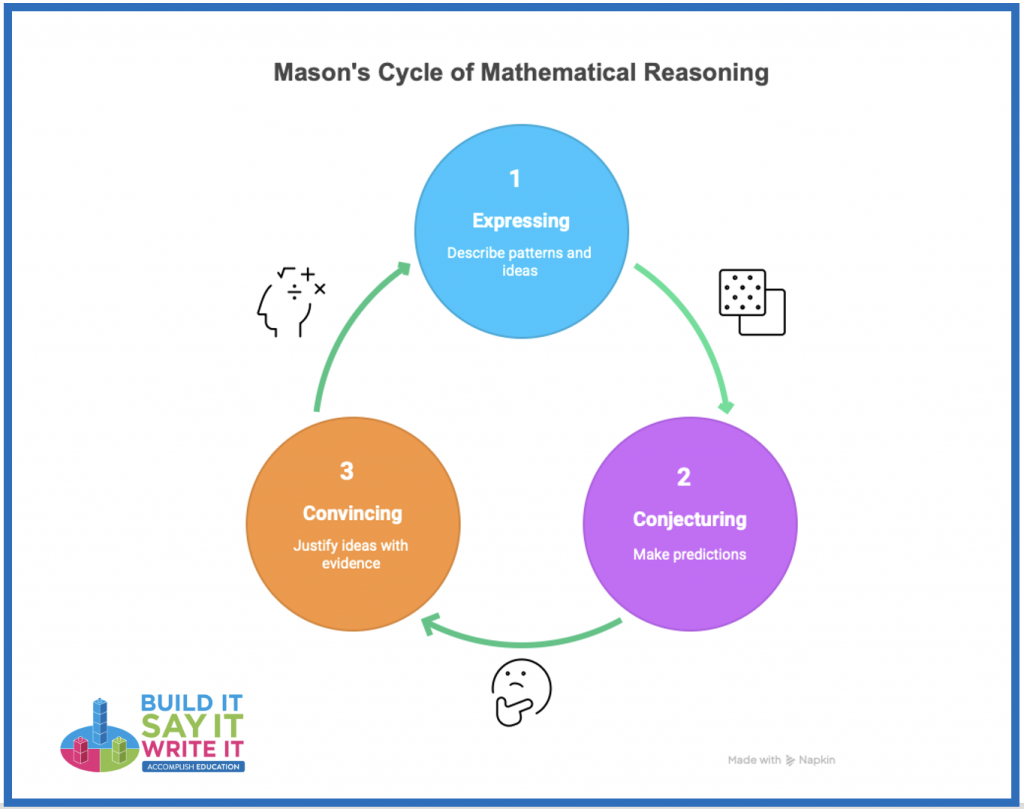
- apply the principles of John Mason’s approach to Problem solving – Thinking Mathematically (Mason, Burton & Stacey) 1982.
Below is an example reasoning and problem solving task which can be readily amended for children of different ages or prior attainments. The example could be used by a teacher to model to children an approach/thinking.
TASK: Two consecutive odd numbers multiply to 399. What are the numbers?
Here is one approach using digital technology – polypad.org/U3ObR7YyGiq5YA
Once opened Click on the play button in the blue recording box to hear and see my thinking, reasoning and ultimately a solution to the problem.
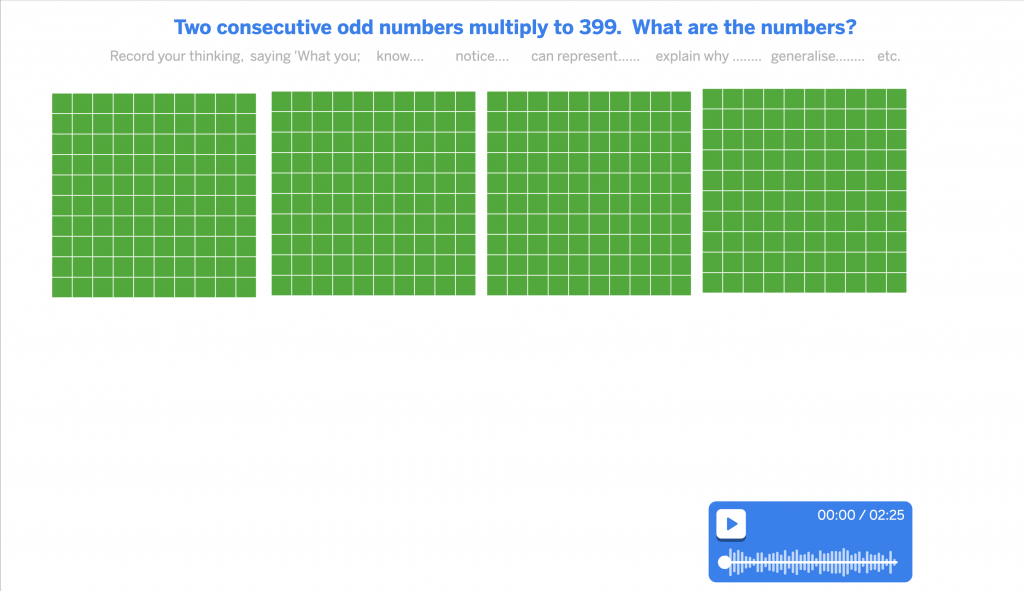
Which of the following features of metacognition have been demonstrated in working on this reasoning and problem solving task?

To be continued.
Leave a Reply